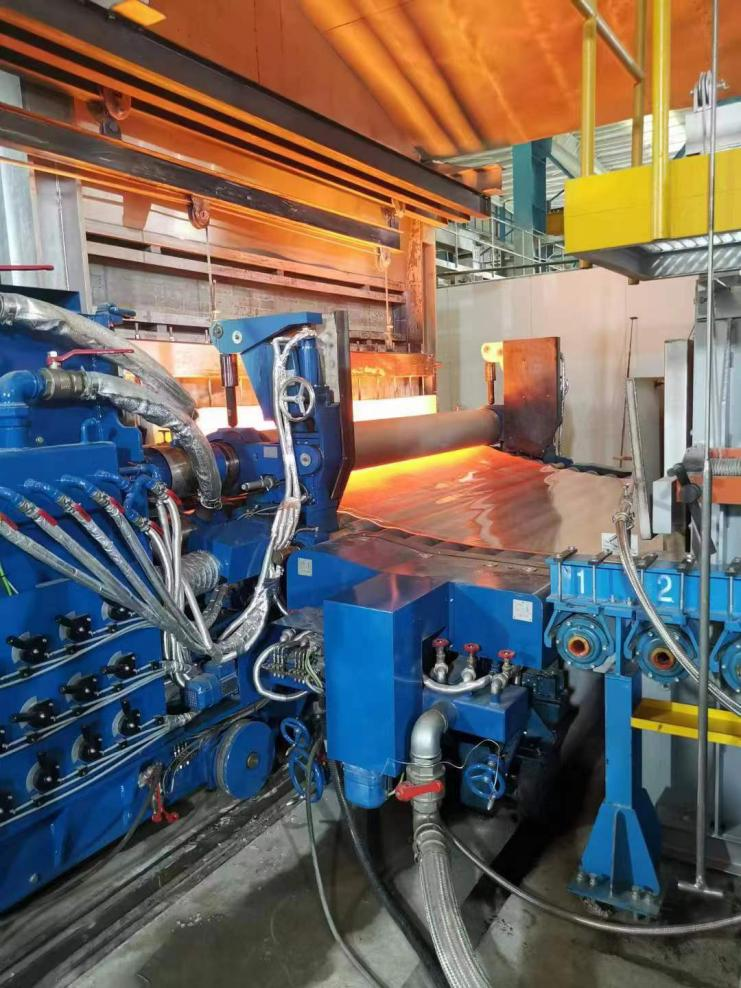
Sikring af sikre driftsforhold i en floatglasfabrik
Sikkerhed i en floatglasfabrik er en grundlæggende bekymring for både ledelsen og medarbejderne. Disse faciliteter involverer meget komplekse processer, herunder smeltning af råvarer ved ekstreme temperaturer, håndtering af store glasplader og drift af automatiserede maskiner. Hver af disse aktiviteter medfører indlysende risici, og gennemførelsen af omfattende sikkerhedsprotokoller er afgørende for at beskytte menneskers liv, forhindre udstyrsskader og opretholde produktiviteten.
Floatglasfabrikker er unikke miljøer, hvor smeltet glas løber kontinuerligt, og arbejdere skal samarbejde med avanceret udstyr. Selv mindre fejl i forhold til sikkerhed kan føre til alvorlige ulykker, dyre nedetid og reguleringsmæssige sanktioner. Derfor fokuserer enhver moderne floatglasfabrik på en flerlaget tilgang til sikkerhed, der kombinerer teknologi, træning og operationel disciplin.
Fordele ved at følge strenge sikkerhedsprotokoller er mangfoldige. De beskytter ikke kun medarbejderne, men forbedrer også driftseffektiviteten ved at reducere afbrydelser, sænke reparationomkostninger og øge anlæggets samlede pålidelighed. At forstå disse protokoller i detaljer giver indsigt i, hvordan en floatglasfabrik fungerer sikkert i hverdagen.
Personlig beskyttelsesudstyr (PPE) og arbejdssikkerhed
Beskyttende tøj og udstyr
I en floatglasfabrik udsættes arbejdere for ekstreme forhold, herunder høje temperaturer, skarpe kanter og smeltet glas. Korrekt beskyttelsesudstyr (PPE) er en nødvendighed. Håndsker der er varmebestandige, hjelme med ansigtsskyd, flammehæmmende tøj og stålskoddede støvler er standardkrav.
Beskyttelsesudstyr er ikke blot en regel, det direkte forhindrer forbrændinger, snit og øjenskader. For eksempel kan splinter fra tempereret glas forårsage alvorlige snitskader, og uden beskyttelsesbriller er risikoen for øjenskader meget høj. Ligeledes forhindrer håndsker og forklder forbrændinger fra varme glasoverflader eller kontakt med ovnkomponenter.
En vigtig del af PPE-overholdelsen indebærer konsekvent brug. Floatglasfabrikker implementerer ofte et overvågningssystem for at sikre, at alle arbejdere bærer det korrekte beskyttelsesudstyr, før de træder ind i områder med høj risiko. Førere udfører rutinemæssigt stikprøver for at sikre overholdelse og fremme en sikkerhedskultur.
Sikkerhedstræning og procedurer
Uddannelse i en floatglasfabrik rækker ud over grundlæggende sikkerhedsinstruktioner. Medarbejderne undervises i brandforebyggelse, håndtering af smeltet glas, sikkert betjening af udstyr og hvordan man reagerer ved kemikalieudslip. Der gennemføres også simulationøvelser, hvor medarbejderne træner evakuering eller akutte nødsituationer i kontrollerede miljøer.
Kontinuerlige uddannelsesprogrammer holder medarbejderne ajourførte omkring de nyeste sikkerhedsteknologier og bedste praksisser. Desuden sikrer introduktionsprogrammer for nye medarbejdere, at de forstår både standardarbejdsprocesser og fabrikspecifikke risikoer. Ved at integrere teoretisk viden med praktisk træning opretholder en floatglasfabrik en arbejdsstyrke, der både er kvalificeret og sikkerhedsbevidst.
Maskinsikkerhed i en floatglasfabrik
Automatiserede beskyttelsessystemer
Avanceret udstyr i floatglasfabrikker, herunder transportbånd, skæremaskiner og robotarme, udgør betydelige risici. Automatiserede beskyttelsessystemer reducerer disse farer ved at bruge sensorer, lysgardiner og interlocks til at forhindre menneskelig kontakt med bevægende dele.
Hvis en arbejder ved en fejl kommer ind i en restricted zone, slukker udstyret automatisk, og skader undgås. Nogle floatglasfabrikker integrerer AI-baserede overvågningssystemer, som kan registrere usædvanlige bevægelsesmønstre og derved yderligere forbedre sikkerheden.
Disse systemer er især vigtige ved skærestationer, hvor automatiserede klinger bevæger sig med høj hastighed, og ved håndteringsrobotter, som manipulerer store og tunge glasplader. Ved at kombinere automatisering med intelligente sensorer reducerer en floatglasfabrik ulykkesrisikoen og opretholder samtidig en høj produktionseffektivitet.
Regelmæssig kontrol af udstyr
Rutinemæssige inspektioner er afgørende for at identificere slitage eller potentielle fejl før de fører til ulykker. Flydende glasværker udfører planlagt vedligeholdelse af hele udstyret, herunder ovne, ruller, skærere og håndteringssystemer.
Inspektionsprotokoller omfatter kontrol af knivskarphed, motorjustering, konsistens af transportbånd og funktion af nødstop. Avancerede anlæg bruger ofte prediktiv vedligeholdelsesteknologi, hvor sensorer indsamler driftsdata for at forudsige udstyrsfejl. Denne proactive tilgang sikrer, at maskinerne fungerer sikkert og reducerer risikoen for uventede nedetider.
Brand- og varmefareforebyggelse
Ovnens sikkerhedsforanstaltninger
Ovnen er hjertet i ethvert flydende glasværk og opnår temperaturer over 1.500°C (2.732°F). Specialiserede sikkerhedsforanstaltninger er kritiske. Varmeskærme, automatiserede kølesystemer og temperaturmålingsudstyr hjælper med at opretholde sikre forhold for arbejdstagerne.
Operatører modtager grundig træning i at håndtere ovnens start, kontinuerlig drift og nedlukningsprocedurer. Alarmsystemer underretter personalet om unormale temperatursvingninger eller potentielle gaslækager, hvilket muliggør øjeblikkelig indsats. Sikkerhedsprotokoller dikterer også minimumsafstande og evakueringszoner i forbindelse med ovnen.
Brandslukningssystemer
Brandfarer i en floatglassfabrik er ikke alene begrænset til ovne. Elektriske fejl, kemiske reaktioner og utilsigtet kontakt med brandbare materialer kan alle udløse brande. For at modvirke dette er omfattende brandslukningssystemer installeret, herunder sprinklere, gasbaserede slukningsmidler og varmeaktiverede alarmer.
Regelmæssig test og vedligeholdelse af disse systemer er obligatorisk. Nogle fabrikker integrerer også automatiserede detekteringssystemer, som udløser alarmer, slukker ovne og frigiver slukningsmidler inden for få sekunder af at have registreret en potentiel brand. Denne lagdelte tilgang sikrer, at både personale og værdifulde udstyr forbliver beskyttet.
Kemisk og miljømæssig sikkerhed
Sikker håndtering af kemikalier
Floatglasværker bruger kemikalier i belægningsprocesser, rengøring og råmaterialeforberedelse. Natriumhydroxid, svovlforbindelser og andre tilsætningsstoffer kræver omhyggelig håndtering. Korrekt opbevaring i mærkede beholdere, sekundære opbevaringssystemer og overholdelse af sikkerhedsdatablade (SDB) forhindrer utilsigtet eksponering.
Arbejdere trænes i korrekt håndteringsprocedurer, herunder hvordan man reagerer over for udslip, indånding eller hudkontakt. Nødskyllesteder og førstehjælpskasser er strategisk placeret i hele faciliteten, hvilket muliggør hurtig behandling af kemikalieincidenter.
Miljøbeskyttelsesforanstaltninger
Miljøsikkerhed er integreret i moderne floatglasværker. Kontrollerede emissionsystemer opsamler partikler, mens vaskere reducerer kemisk udledning til atmosfæren. Spildevand behandles, før det udledes, og bæredygtige råmaterialer reducerer værkets samlede miljøpåvirkning.
Energioptimering fremhæves også. Avancerede ovne og varmegenvindingssystemer reducerer energiforbruget og mindsker varmeudledning, hvilket bidrager til en sikrere arbejdsplads. Ved at kombinere miljøbeskyttelse med arbejdssikkerhed fremmer en floatglasfabrik en ansvarlig og sikker driftsmodel.
Beredskab og risikostyring
Nødhandslingsplaner
Hver floatglasfabrik har en detaljeret nødhandslingsplan. Denne omfatter evakueringsruter, kommunikationsprotokoller, samlingsteder og fastlagte ansvarsområder for ledere og medarbejdere.
Almindelige øvelser gør medarbejderne fortrolige med nødprocedurer. I nogle faciliteter simuleres øvelser ovnunderskud, kemikaliespild eller udstyrsfejl, så medarbejderne kan reagere hurtigt og passende for at minimere skader og udstyrsskader.
Risikovurdering og løbende forbedring
Floatglassfabrikker udfører løbende risikovurderinger for at identificere nye farer og forbedre sikkerhedsprotokoller. Dette omfatter analyse af nær-uheld, udstyrsfejl og mønstre i menneskelige fejl.
Moderne faciliteter anvender også IoT-baseret overvågning og prediktiv analyse til at identificere potentielle risikoer, før de eskalerer. Ved løbende forbedring sikres, at en floatglassfabrik tilpasser sig ændrede sikkerhedsstandarder, teknologiske fremskridt og driftsmæssige ændringer.
Ofte stillede spørgsmål
Hvad er de væsentligste sikkerhedsforanstaltninger i en floatglassfabrik?
Nødvendige foranstaltninger omfatter brug af personlig beskyttelsesudstyr (PPE), grundig arbejdstræning, automatiserede maskinbeskyttelsesanordninger, rutinemæssige udstyrskontroller, ovn- og brandsikringssystemer, kemikalierhåndteringsprotokoller samt miljøbeskyttelsesforanstaltninger.
Hvordan forebygger en floatglassfabrik brandfarer?
Ovne er udstyret med varmeskærme og overvågningssystemer, mens brandbekæmpelsesmekanismer omfatter sprinklere, gasslukningsudstyr og automatiserede nedlukningssystemer til hurtig respons.
Er miljøsikkerhedsprotokoller en del af en floatglassfabrik?
Ja. Kontrollerede emissioner, korrekt affaldshåndtering, energieffektiv drift og bæredygtig anvendelse af materialer hjælper med at opretholde både miljø- og arbejdssikkerhed.
Hvordan forbedrer beredskab sikkerheden?
Beredskehed planer, rutinemæssige øvelser og proaktive risikovurderinger gør det muligt for medarbejdere at handle hurtigt og reducere potentielle skader eller skader under ulykker eller uventede hændelser.
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 MT
MT
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 SW
SW
 GA
GA
 AZ
AZ
